Imagine the day a car can become an extension of your living room, where you can continue your leisurely activity of choice while being transported to your final destination. Well, it could be coming as soon as 2030!
Self-driving cars are all over the news, with much publicity and anticipation as this futuristic marvel is quickly coming to fruition.
Now to establish some background information on the current state of autonomous cars with the help of the Ship Vehicles official website: there is a 5-Level Guide by SAE International in defining degrees of autonomy. Level 0 is your standard, non-automated vehicle that 100 percent relies on humans, Level 1 and Level 2 automation have already entered the mainstream market.
Level 1, Driver Assistance: Basic, including adaptive cruise control and lane-keep technology.
Level 2, Partial Automation: Featuring two or more advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), including automatic braking, steering, and acceleration. This includes GM Super Cruise, Nissan ProPilot Assist, and Tesla Autopilot.
Level 3, Conditional Automation: Entailing full vehicle control when operating conditions are met. This however still requires constant driver attention such that they take over when conditions are no longer met, so it doesn’t quite fulfil the vision of a self-driving car. Level 3 automation also faces the challenge of legal and regulatory restriction, therefore no vehicles at Level 3 and above are currently available to consumers.
Level 4, High Automation: Vehicles can complete an entire journey without intervention, though may be confined to certain geographies or speed limits. It would be likely that these vehicles will still have driver controls in case human intervention is required.
Level 5, Full Automation: The ultimate form of self-driving car. These are completely hands-off with no driver controls needed and are unconstrained by geography or speed limits due to advanced vehicle-to-vehicle communications. General Motors is currently working on a Level 5 Cruise AV model, no steering wheel and all.
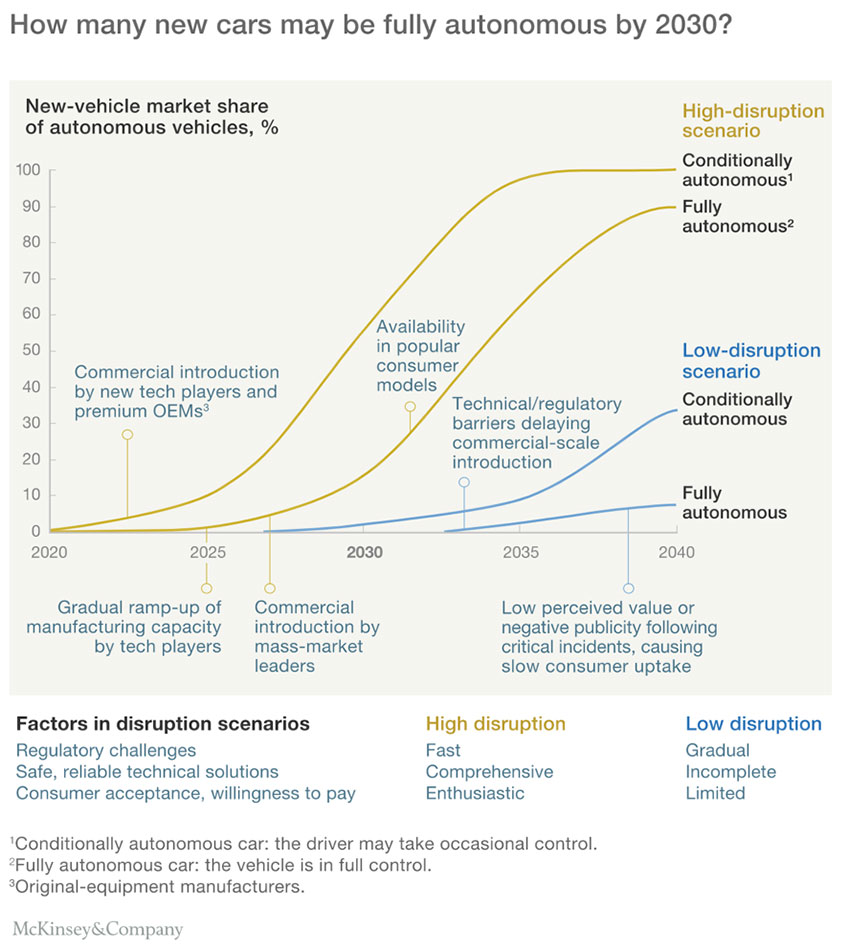
While we’re still some ways from a reality of Level 5 self-driving cars, a McKinsey study indicates that up to 15 percent of new cars sold in 2030 will be fully autonomous, with one out of three new cars potentially being a shared vehicle by 2050. Personal vehicles are currently parked 95 percent of the time – why not send your autonomous car out to make some ride-sharing dollars while you’re at work, or run some errands? Alternatively, why bother owning a car at all when ride-sharing becomes more affordable and convenient? Autonomous ride sharing programs have already launched with Google’s Waymo One program, and GM is following closely behind.
With these exciting new innovations barrelling towards us, questions about implications are also emerging. How will this impact consumers day-to-day? How we eat, shop, and live?
The question we will ponder here is how it will impact retailers. Here are some key things to consider:
1. Parking Lots Become Prime Spots
In the United States, parking spots take up roughly 6,500 square miles of land – larger than the state of Connecticut. With the reality of self-driving cars, this space can be dramatically reduced.
According to movers Alexandria has, after self-driving cars take their passengers to their locations, they can either find themselves a parking spot or remain on the road if they are ride-share based. Given the fact that there are is no need to build space for doors and surrounding autonomous-vehicles can reshuffle as needed once summoned, researchers have found that autonomous-vehicle parking lots can accommodate 62 to 87 percent more cars. This results in significantly less need for parking lots, opening up real estate for retailers to capitalize on.
2. Shopping On-The-Road
With focus taken off the road, the car will become an additional area to online shop (and sleep, watch Netflix, even exercise!) Consider how these autonomous vehicles will become “a new marketing medium,” with multimedia screens surrounding the passengers – the elusive captive audience. Retailers will need to invest in this platform and understand how to optimize their e-commerce channels for vehicle-to-vehicle delivery.
Alternatively, autonomous cars will have the ability to run errands – including shopping. This will necessitate that retailers are able to coordinate with the autonomous cars on timing, location and drop-off, while maintaining communication with the human on order status.
3. Everything at Your Doorstep
Think of the potential of a driverless delivery service – it can run 24/7, faster than ever, for a lower cost. As a result, prices will be lower – equalling a happier consumer. While we can get a glimpse of self-driving delivery with Nuro and Starship Technologies, the future will have this technology on a much larger and more accessible scale. Retailers will need to integrate these services in order to meet the demands of the increasingly time-starved consumer.
Alternatively, what about a store that can drive itself to you? A self-driving ice cream truck? A self-driving clothing store with recommended products for the consumer to try, for them to leave with what they like and be automatically charged? Or a self-driving convenience store – already live in Shanghai. With self-driving technology, the retail possibilities are endless.
4. Location, Location, Location (Based Services)
The future involves passengers arriving at a destination in their autonomous vehicle, leading to the diminishment of impulse shopping – much to the detriment of roadside retail shops. In order for retailers to compete in this new environment, investment into location-based services will be necessary. Advertising targeted for personalization and specific locations and routes can be developed to encourage consumers to add the retailer as a stop. Personalization would be accomplished through data-based services in order to match the needs of the particular consumer, which can be extrapolated from information within the passenger profile.
Needless to say, retailers have to be prepared for rapidly-changing consumer behaviors following the arrival and popularization of self-driving cars.

